causes of psoriasis
- Genetic predisposition – Scientists have described a number of genes whose presence predisposes to the development of disease;
- endocrine, immune, and nervous system dysfunction;
- negative effects of certain environmental factors.
- Chronic infectious diseases (most commonly caused by streptococci);
- Alcoholism, chronic alcoholism;
- Weather conditions (dry or cold climates);
- Skin trauma (scratches, insect bites, sunburn);
- often emotionally stressed;
- taking certain medications (e. g. , lithium, adrenergic blockers, oral contraceptives, antimalarials);
- Abrupt discontinuation of systemic hormonal medications.
stages of psoriasis
- Progressive - characterized by an increase in the number of rash components, fusion of papules, and the appearance of new components at the injured site. The patches are bright pink and covered with scales. The cell division rate of new lesions increases 10-fold;
- Quiescent - no fresh elements are observed, the plaques are stagnant red, there is little peeling, the itching is hardly bothersome;
- Regression - the intensity of the color of the rash decreases, the components of the rash are pale, no new rash appears, no peeling, no subjective signs are noted. A white pseudoatrophic rim forms around the plaque, and healthy skin appears in the center of the large plaque. Colorless spots remain at the rash site.
disease symptoms
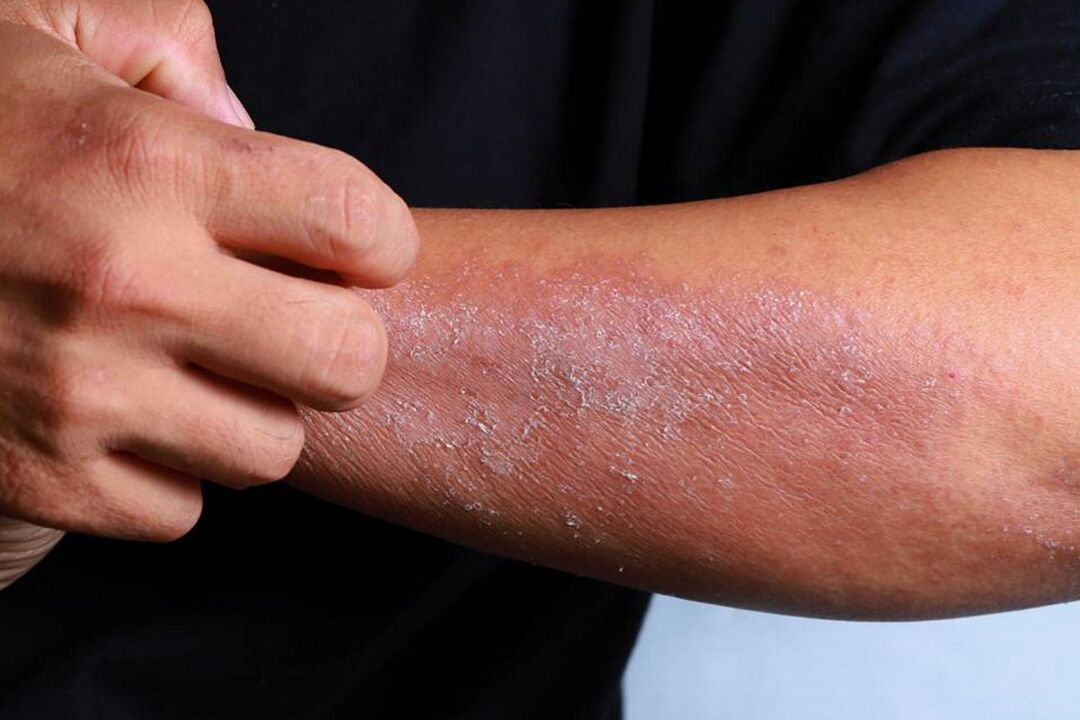
- Rashes - they always appear in one form or another;
- The skin in the psoriasis area feels tight;
- Varying degrees of itching.
- Scalp (with this arrangement of plaques we are talking about seborrheic psoriasis);
- knees and elbows;
- skin folds and flexor surfaces - elbow joints, knees, groin, axillary area, under the breast (this positioning allows us to talk about inverse psoriasis);
- lumbar spine, sacrum;
- Palms and feet - with palmoplantar psoriasis, respectively;
- Nail psoriasis – Dimples on the nail plate, subungual bleeding, and separation of the nail from the nail bed (onycholysis).
Types of psoriasis
psoriasis erythroderma
psoriatic arthritis
diagnosis
treat
Using laser devices to treat psoriasis
- psoriasis;
- Vitiligo;
- Atopic dermatitis;
- Patchy alopecia (hair loss);
- Change in scar color;
- eczema.
- Pregnant;
- neoplastic diseases;
- The general condition is serious.
Why we should pay attention to systemic treatment
- The effects are localized, targeting only the psoriasis plaques, and the rays do not affect the entire body;
- In mild cases, stable remission can be achieved with only phototherapy and photosensitizers;
- Suitable for patients of any age (from 3 years old);
- Laser system treatment does not require hospitalization and can be easily adapted to any work schedule;
- Effective against many forms of psoriasis;
- Minimum limit.
How does the treatment process work?
psychological aid
Benefits of treating psoriasis in the clinic
- Experienced, qualified dermatologists and beauticians;
- Eliminates skin and cosmetic problems simultaneously;
- Innovative treatment methods, especially the use of laser systems;
- The most modern diagnostic methods;
- Opportunity to consult with doctors from various specialties.
Prevent psoriasis
- Prevent stress;
- Prevent colds;
- Control chronic infection lesions;
- Refuse to wear rough, tight clothes that can damage your skin.